WELCOME TO RACHEL’S BLOG
Scroll down to see the most recent posts, or use the search bar to find previous blogs, news, and other updates

The Saxon Secret to Avoiding a Bad Ruler
What if the worst rulers in English history didn't have to happen?
Bad kings - the weak, the cruel, the catastrophically incompetent - weren't inevitable. They were the consequence of a system that handed the most powerful job in the kingdom to whoever happened to emerge from the right womb in the right order!
Primogeniture, succession by (male) birth order, gave England Edward II, whose personal failings and political incompetence ended in his deposition and probable murder. It gave England Richard II, whose erratic tyranny triggered a constitutional crisis and cost him his throne. It gave England Henry VI, whose mental collapse plunged the country into thirty years of civil war. These weren't accidents of fate. They were what happens when a system prioritises birth order over every other human quality.
But before the Normans locked this system in place, the Anglo-Saxons did something far more interesting.
The Aetheling System: Choose the Best, Not the First

Nicola de la Haye
The inspiration of Brienne of Tarth, Nicola de la Haye saved England twice. Watch the video below and discover the legend. (Spoilers alerts!).
And when you’ve finished, it’s time to find out more about the medieval heroine, the world she lived in, the corrupt men she had to deal with, and how the medieval badass sorted them all out!
Buy the first book in the Nicola de la Haye series, Lady of Lincoln, here.

Fastrada: Charlemagne’s Queen History Tried to Forget
Charlemagne is usually thought of as the iron-willed king, crowned Emperor of the Romans in 800, architect of a European empire and champion of learning and reform. What we never hear about, however, are the women who stood beside him: women whose influence shaped politics, justice, and the fragile stability of his realm.
One of the most controversial of these women was Fastrada, Charlemagne’s fourth wife and queen, a woman remembered less for what she did than for how male chroniclers chose to describe her.
A Frankish Noblewoman in a Dangerous Court
Fastrada was born into the high Frankish nobility around the mid-8th century, the daughter of Count Radulf. Her marriage to Charlemagne in 783 was not a romantic match but a strategic one, strengthening ties between powerful families within the Frankish heartlands. This was a period when Charlemagne’s empire was expanding rapidly through conquest, forced conversion, and ruthless suppression of revolt.
Queens in the Carolingian world were not crowned consorts in the later medieval sense, but they were far from ornamental. They managed households, acted as intermediaries, dispensed patronage, and, crucially, advised the king. Fastrada arrived at court at a moment when Charlemagne’s rule was under strain from internal rebellion, particularly in Saxony.
“Cruel” Queen or Convenient Scapegoat?
Our surviving sources paint Fastrada in dark colours. Einhard, Charlemagne’s biographer, describes her as harsh and cruel, claiming that her influence made the king more severe in judgement. Later chroniclers echoed this, blaming her for brutal punishments meted out against rebels and dissenters.
But this raises an uncomfortable question: Was Fastrada truly cruel, or was she blamed for decisions Charlemagne himself made?
Early medieval queens were often held responsible when kings ruled harshly. Advising firmness could easily be reframed as bloodthirstiness, especially when the adviser was a woman. Fastrada’s reputation may tell us more about medieval anxieties over female influence than about her actual character.
It is worth noting that Charlemagne’s most notorious acts of brutality, including the mass executions of Saxons, predated and outlasted Fastrada’s life. Yet only she became a symbol of excessive severity.

Novel Title Announcement on Michaelmas
In just one week, on Michaelmas (29 September), a day of great significance in the medieval world, I’ll be unveiling the title of my debut historical novel about the formative years of Nicola de la Haye, ‘The Woman who Saved England."‘
It’s a story of castles under siege, dangerous rebellions, and the woman history tried to silence… but who could not be erased.
Stay tuned for the title reveal!

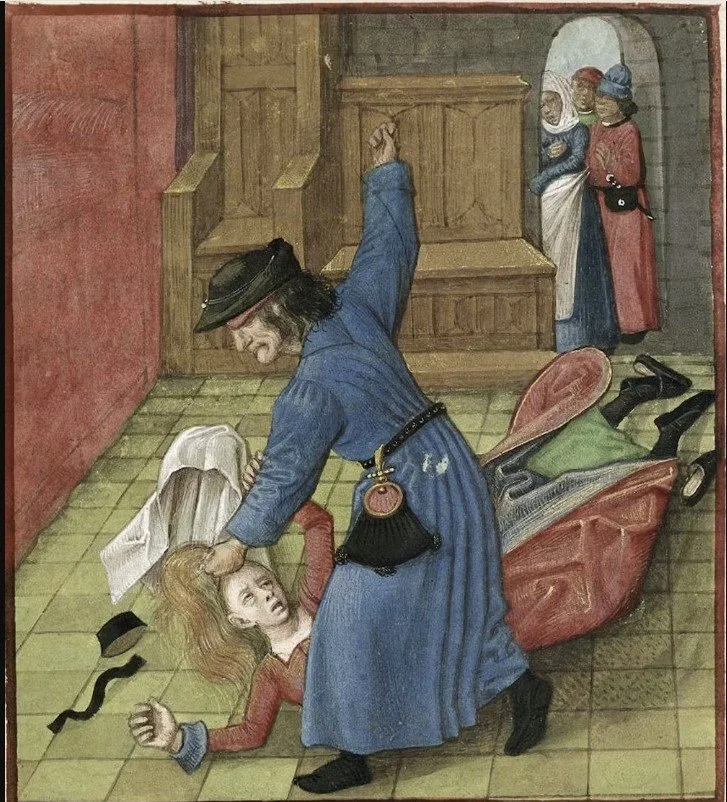
Philippe II (Augustus) of France Humiliated Queen Ingeborg
A Wedding Day Turned Nightmare
On 14 August 1193, the cathedral at Amiens was filled with splendour. Nobles crowded in, candles glowed, and choirs sang as King Philip II of France — called Augustus for his ambition — married Ingeborg of Denmark, a daughter of King Valdemar I.
It was a diplomatic triumph. The marriage would secure French ties to Denmark, giving Philip allies in the north and prestige across Christendom. Ingeborg, known for her piety and education, arrived prepared to be queen of France.
But before the day was out, her life turned into a nightmare.
Medieval Misogyny: Five Men Who Made Women’s Lives Miserable
This blog series uncovers the darker side of 12th-century power: the men whose actions towards women were so cruel that even their contemporaries condemned them.

Geoffrey of Anjou: The Handsome Count Who Founded the Plantagenet Dynasty (Died 7th September 1151)
On September 7, 1151, Geoffrey of Anjou — known as “le Bel” or “the Handsome” — collapsed with a sudden fever and died at just 38 years old.
He was never king. He never wore a crown.
And yet, Geoffrey Plantagenet shaped the medieval world more than many monarchs.
Without him, there would be no Henry II, no Richard the Lionheart, no King John and Magna Carta, and no centuries-long Plantagenet dynasty. Geoffrey’s story isn’t just a footnote — it’s the spark that set medieval England ablaze.

The Secret Is Out: The Heroine of Rachel’s Upcoming Novel is… Nicola de la Haye
My protagonist is Nicola (Nicholaa) de la Haye: the woman who saved England.
Nicola isn’t a creation of legend or folklore. She was real — a formidable 12th- and 13th-century noblewoman who defied the expectations of her age. She inherited power in her own right, commanded a castle garrison, and twice (at least) defended Lincoln Castle from siege.
Most famously, in 1217, when England teetered on the edge of conquest by Prince Louis of France, Nicola — then nearly seventy years old — refused to surrender her castle. She held the fortress until William Marshal’s army turned the tide in what chroniclers called the Battle of Lincoln Fair (or the Second Battle of Lincoln). Without her, England’s story might have ended very differently.

She Wasn’t Supposed to Matter…
She didn’t set out to defy anyone. She didn’t burn with ambition, or plot her way to power. She was young. She wanted love. She was raised to trust men to handle the weight of responsibility. And yet, by the time her story was done, she’d held command of one of England’s greatest castles, faced down rebellions, navigated the treachery and ambition of the marriage market, and made choices that shaped the future of a kingdom.

The Battle of Fornham: When a Countess Rode to War and Changed Medieval England Forever
In the mist-shrouded dawn of October 17, 1173, near the quiet Suffolk village of Fornham St. Genevieve, history was about to witness something remarkable. Not just another medieval battle between king and rebels, but the extraordinary tale of a countess who donned armor, took up lance and shield, and rode into battle alongside her husband against the Crown itself.
This is the story of Petronilla de Grandmesnil, Countess of Leicester – a woman whose courage would echo through the centuries, and whose fall into a muddy ditch would become one of the most memorable moments of medieval English warfare.
